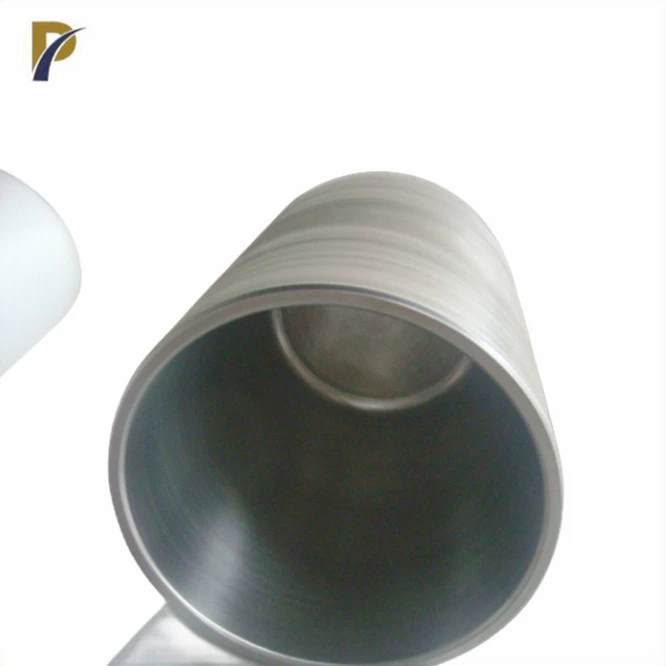
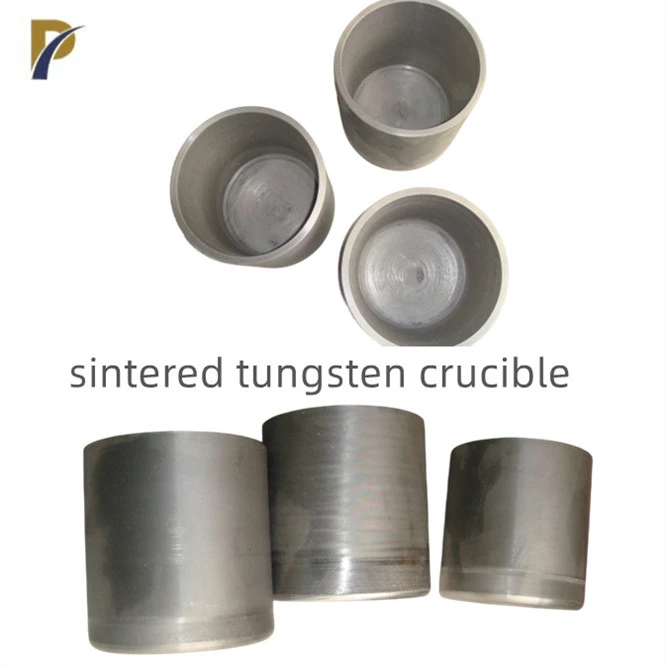
Tungsten crucibles, renowned for their exceptional heat resistance, can withstand temperatures up to 3,400°C (6,152°F) without melting. This remarkable heat tolerance is due to tungsten's incredibly high melting point of 3,422°C (6,192°F), the highest of any metal. In practical applications, tungsten crucibles are typically used at temperatures ranging from 2,000°C to 3,000°C (3,632°F to 5,432°F), providing a wide operational range for various high-temperature processes. Their ability to maintain structural integrity and chemical inertness at these extreme temperatures makes them invaluable in industries such as metallurgy, electronics, and advanced materials research.
The Exceptional Heat Resistance of Tungsten Crucibles
Unparalleled Melting Point
Tungsten is distinguished by its extraordinary melting point of 3,422°C, one of the highest among all known metals. This unique property enables tungsten crucibles to maintain their shape and mechanical integrity in thermal environments where many other refractory metals would soften, deform, or even vaporize. Such stability is particularly vital in high-temperature operations, including the production of superalloys, the sintering of advanced materials, or the growth of single crystals used in electronics. These applications demand a container that can withstand prolonged exposure to extreme heat without degradation.
Thermal Stability and Low Expansion
In addition to its unmatched melting point, tungsten demonstrates remarkable thermal stability, making it a preferred material for precision applications. One of its key advantages is a very low coefficient of thermal expansion, which means that dimensional changes under heating are minimal. This property ensures that tungsten crucibles retain their exact geometries even during repeated heating and cooling cycles. As a result, industries such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD), high-temperature research, and precious metal melting benefit from consistent results and reduced risk of component failure or dimensional inaccuracies.
Chemical Inertness at High Temperatures
Another defining characteristic of tungsten is its exceptional chemical inertness, even when exposed to elevated temperatures. Unlike other metals that may react with or contaminate the materials being processed, tungsten resists oxidation and chemical attack under controlled atmospheres. This stability is critical for industries that require ultra-pure processing environments, including semiconductor fabrication, advanced ceramics production, and specialty chemical research. By preventing impurities from entering the processed material, tungsten crucibles ensure high purity standards, making them indispensable in applications where contamination control is a top priority.
 |
 |
Applications Leveraging Tungsten Crucibles' Heat Resistance
Metallurgical Processing
In the metallurgical sector, tungsten crucibles are indispensable tools for handling high-temperature metals and alloys that cannot be processed using conventional materials. Their unmatched ability to endure extreme heat enables the melting, refining, and alloying of elements such as molybdenum, tantalum, and niobium. These metals are critical in producing superalloys used in demanding fields such as aerospace, defense, and power generation. By maintaining structural integrity and resisting contamination at extreme temperatures, tungsten crucibles ensure consistent results, making them vital for achieving reliable performance in advanced metallurgical applications.
Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The semiconductor and electronics industries rely on tungsten crucibles for several high-precision processes that demand both heat resistance and material purity. One of their most critical roles lies in the controlled growth of single-crystal materials such as silicon, gallium arsenide, and sapphire, which serve as the foundation of electronic devices. The crucibles’ exceptional thermal stability prevents distortion and ensures defect-free crystal structures. Additionally, their chemical inertness minimizes contamination risks, enabling the production of high-performance semiconductors that meet the strict quality requirements of microelectronics, optoelectronics, and advanced communication technologies.
Advanced Materials Research
In scientific research and advanced materials development, tungsten crucibles provide the durability and reliability required for experiments involving extreme thermal environments. Laboratories use them to synthesize new compounds, explore innovative alloys, and investigate advanced ceramics under conditions that exceed the capabilities of most other crucible materials. Their resilience allows researchers to push the boundaries of energy storage solutions, superconducting materials, and nanostructured systems. By enabling experiments at very high temperatures without compromising purity, tungsten crucibles play a pivotal role in accelerating discoveries that drive technological innovation across multiple emerging industries.
 |
 |
Factors Influencing Heat Resistance in Tungsten Crucibles
Purity and Composition
The heat resistance of tungsten crucibles is directly related to their purity. Higher purity tungsten exhibits better heat resistance and chemical inertness. Impurities can lower the melting point and introduce weak points in the crucible structure. Therefore, manufacturers like Shaanxi Peakrise Metal Co., Ltd. focus on producing crucibles with purities of 99.95% or higher to ensure optimal performance under extreme temperatures.
Manufacturing Process and Microstructure
The method used to manufacture tungsten crucibles significantly impacts their heat resistance. Advanced techniques such as powder metallurgy and sintering processes can create crucibles with optimal grain structures and densities. These refined manufacturing methods result in crucibles with enhanced strength and uniformity, capable of withstanding higher temperatures without deformation or failure.
Surface Treatment and Coatings
While pure tungsten already possesses excellent heat resistance, certain surface treatments or coatings can further enhance this property. For instance, some tungsten crucibles may be treated to create a protective oxide layer, which can improve resistance to certain types of chemical attack at high temperatures. These treatments can extend the lifespan and performance of tungsten crucibles in specific high-temperature applications.
Conclusion
Tungsten crucibles stand as marvels of material science, capable of withstanding temperatures that few other materials can endure. Their ability to maintain structural integrity and chemical inertness at temperatures up to 3,400°C makes them invaluable in a wide range of high-temperature applications. From metallurgical processing to advanced materials research, tungsten crucibles enable processes and discoveries that push the boundaries of technology and science. As industries continue to demand materials capable of withstanding ever more extreme conditions, the role of tungsten crucibles in advancing technological progress remains secure.
FAQs
What is the maximum temperature a tungsten crucible can withstand?
Tungsten crucibles can withstand temperatures up to 3,400°C (6,152°F) without melting, thanks to tungsten's high melting point of 3,422°C (6,192°F).
Are tungsten crucibles suitable for all high-temperature applications?
While highly versatile, tungsten crucibles may not be suitable for applications involving strong oxidizing environments at high temperatures.
How does the purity of tungsten affect crucible performance?
Higher purity tungsten (99.95% or above) offers better heat resistance and chemical inertness, crucial for extreme temperature applications.
Experience Unmatched Heat Resistance with Peakrise Metal Tungsten Crucibles
At Shaanxi Peakrise Metal Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on manufacturing tungsten crucibles that set the industry standard for heat resistance and quality. Our state-of-the-art production facilities and rigorous quality control ensure that each crucible meets the most demanding specifications. Whether you need crucibles for metal smelting, semiconductor production, or cutting-edge research, our team is ready to provide tailored solutions. Experience the difference that premium tungsten crucibles can make in your high-temperature processes. Contact us at info@peakrisemetal.com to discuss your specific needs and discover how our products can elevate your operations.
References
"Tungsten: Properties, Chemistry, Technology of the Element, Alloys, and Chemical Compounds" by Erik Lassner and Wolf-Dieter Schubert
"Refractory Metals and Alloys" by C.T. Sims and W.C. Hagel
"High-Temperature Materials and Mechanisms" edited by Yoseph Bar-Cohen
"Materials for High Temperature Engineering Applications" by G.W. Meetham
"Handbook of Refractory Carbides and Nitrides" by Hugh O. Pierson
"Thermal Properties of Matter" by National Physical Laboratory, UK
